What is Composition in Textiles?
A fabric’s composition is a reference to the percentage by weight of each fiber making up that fabric. For example if you have a fabric which is 200gsm (grams per square meter) which is listed as 65% polyester and 35% cotton; this would mean that for every 200gsm of fabric, 130 grams is made of polyester fibers and the remaining 70 grams is made of cotton.
Let us take a closer look at the different fibers on offer, as well as the pro’s and con’s of each…
-
Polyester is one of the most widely used fibers in the world of workwear. It is economical, durable, lightweight, shrink and wrinkle resistant, and easily dyed.
However, drawbacks include a lack of breathability and its environmental impact. Aratex has been proactive to mitigate these environmental concerns with its sustainable fabric initiative which can be found on our homepage! -
Everybody loves cotton. It’s natural, soft, breathable, and absorbent. Cotton is also an excellent choice for sensitive skin as it is naturally hypoallergenic.
However, consumers must be careful when opting for cotton rich fabrics. Cotton tends to not hold dye as well as polyester and so the color will fade over time. Other issues are a lack of durability and poor resistance to wrinkling and shrinkage. Cotton fabrics are delicate and require extra attention. -
Viscose is a semi-synthetic fabric made from wood pulp. It is classified as semi-synthetic due to the chemical processes involved to produce it.
Viscose is naturally water absorbent and breathable. It is also known for its softness and ability to hold dye.
The main drawback with viscose is the environmental impact it causes; namely with regard to deforestation. This is why consumers must take care to ensure the viscose they are buying comes from sustainable harvesters.
But what is yarn? How does it relate to fabrics in a practical sense?
Yarn is defined as a length of interlocked fibers that is used in the production of textiles; both in weaving and knitting. Yarn can be categorized as ‘single’ or ‘plied’.
-
Also known as ‘one-ply’. single yarns are composed of fibers held together with a small amount of twist. When it comes to synthetic material, the filaments are grouped together either with or without twist.
-
Plied yarns are made by twisting together two (two-ply) or more single yarns. These give the yarn more robustness, provide more texture, and are less likely to suffer from pilling.
Let us take a closer look at what makes up the yarn. These are called Fibers.
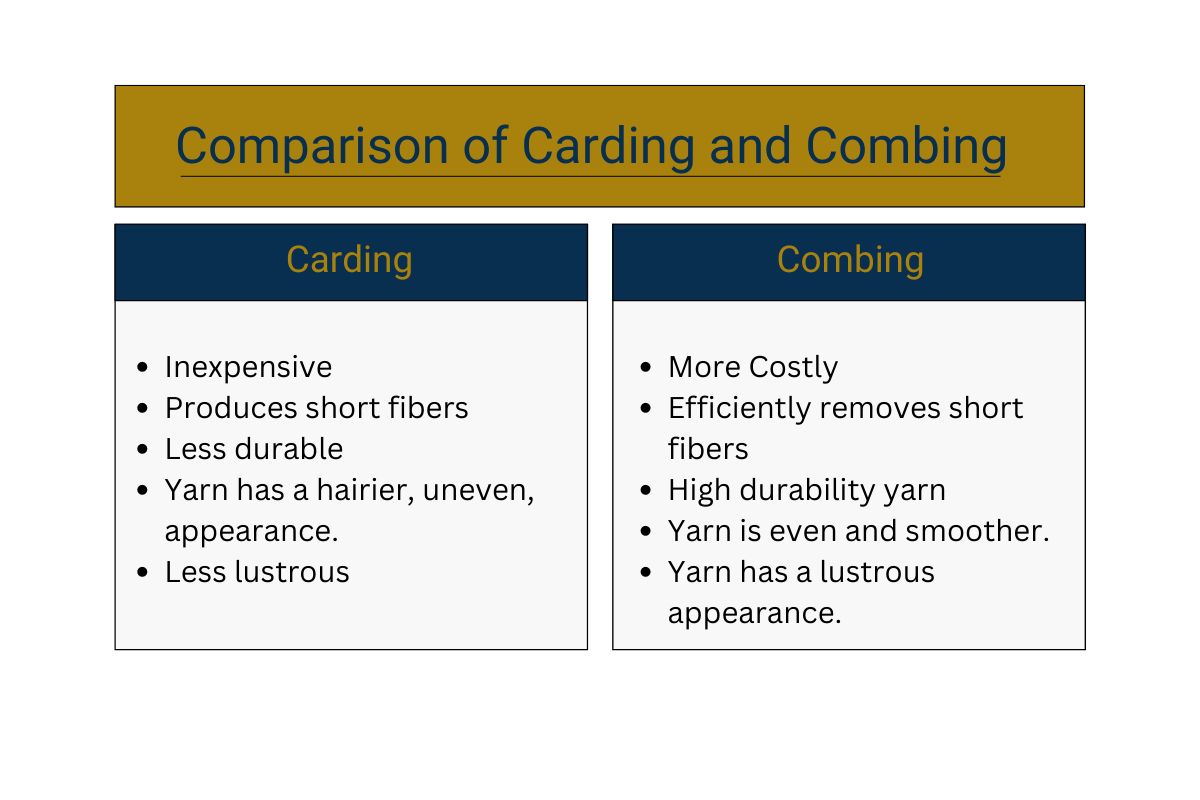
A textile fiber is a unit of material that can be either natural or synthetic, which forms the most basic element of textiles. These are processed into yarn, which in turn are then woven or knitted together to create a fabric cloth. When processing fibers into yarns, two main methods exist. These are called ‘carding’ and ‘combed’. Let us examine these methods below.
-
Carding is a key process in the spinning of fibers into yarn. It does this by opening lumps of fiber into individual ones. This lowers impurities and removes dust via friction. The process also helps to remove some neps (entangled fibers) brought about by opening entanglements.
-
Combing fibers into yarn follows the same procedures as carding, however it goes through further processing by introducing extra steps to ‘comb’ through the fibers. This has several advantages as can be seen below.